This robot is operated by radio frequency, using an RF transmitter and RF receiver.
Radio Waves Versus Sound Waves
There are two types of waves: sound waves and radio waves. Sound waves need a median to propagate while radio waves are independent of a median. That’s why space shuttles and rovers operate with radio frequency. My project is also operated by radio frequency, using two very important components that make up an RF module: the RF transmitter and RF receiver.
Scientific Principle
This project is based on communication through an RF Module from the RF transmitter to the RF receiver.
How Does the Radio-Controlled Robot Work?
Here we will be using a couple of ICs and a motor fixed to a chassis to make our radio controlled-robot. The brief idea is to transmit control signals through radio waves and receive them by receiver module, which is situated in the robot itself. We have four switches on the transmitter section to power each motor for bidirectional motion. The data from the transmitter is encoded before transmission, then received by the receiver, then decoded to be sent to the motor driver (L293D). This is achieved using a radio frequency module, the encoder and decoder, and motor driver (L293D).
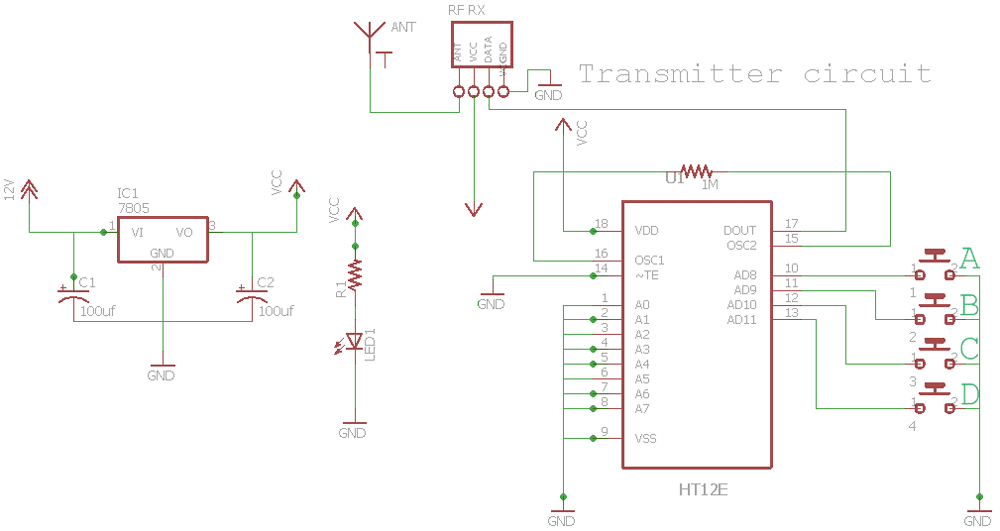
Transmitter Circuit Diagram
Receiver Circuit Diagram
Connect your two separate circuits on two breadboards based on the schematic diagrams above after you have read through the functions of each of the components that are given below.
Important Components and Their Functions
RF Module
The Radio Frequency module consists of a transmitter and a receiver. The pair of modules operates at 434MHz. The frequency acts like a password between both modules. If the frequencies of both modules do not match, then the circuit will not work. The RF transmitter receives serial data from the encoder and transmits it wirelessly. The transmission occurs at a rate of 1kbps–10kbps. The transmitted data is received by the RF receiver operating at same frequency as the transmitter. The wireless data is converted into serial data by the decoder.
Motor Driver (L293D)
The motor Driver (L293D) is a 16pin IC with eight pins on each side dedicated to controlling a DC motor at the same time in both directions. it has two input pins for each motor and one enable pin for each motor. The L293D is what's called an H-BRIDGE.
L293D Motor Driver Circuit
Encoder (HT12E)
An encoder is a device, circuit, transducer, software program, algorithm, or person that converts information from one format or code to another. The encoder’s purpose is to standardize, speed, secure, or save space by shrinking size. Encoders are combinational logic circuits and have the opposite function of decoders. Encoders accept one or more inputs and generate a multibit output code.
Decoder (HT12D)
A decoder can take the form of a multiple-input, multiple output logic circuit that converts coded inputs into coded outputs, where the input and output codes are different (for example n-to-2n, binary-coded decimal decoders). Decoding is used for applications like data multiplexing, seven-segment displays, and memory address decoding.
Potential Applications
Although radio-controlled machines are nothing new, they are still used in many different applications. Here are some applications and industries that still use good old radio waves!
- The majority of space probes, rovers, and spaceships to the other planets in our solar system have been radio controlled, because they work through radio waves. Radio waves are independent of a median, which is helpful, since sound waves can’t travel through space.
- Industrial settings like factories and warehouses use radio waves to carry heavy loads from one place to another.
- Spy agencies still use radio waves.
- Radio-controlled machines are used to get in small spaces where human hands cannot reach.
Enjoy making your own radio-controlled robot!